-
[M(CO)4PPh3]·- radicals (M = Cr, Mo, W): DFT and single crystal EPR investigations
T. Berclaz, B. Ndiaye, S. Bhat, A. Jouaiti and M. Geoffroy
Chemical Physics Letters, 440 (4-6) (2007), p224-228


DOI:10.1016/j.cplett.2007.04.052 | unige:3595 | Abstract | Article HTML | Article PDF
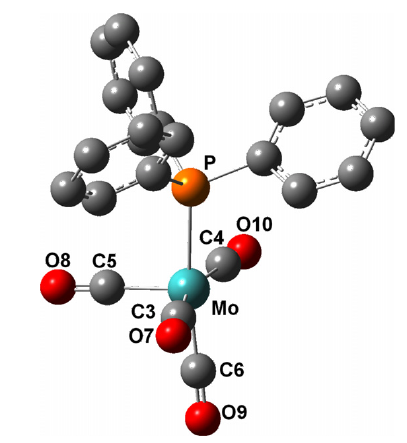
[M(CO)4PPh3]•− (M = Mo, W) were trapped at 77 K in X-irradiated single crystals of M(CO)5PPh3 and studied by EPR. Structures of [M(CO)4PPh3]•− (M = Cr, Mo, W) were optimized by DFT; predicted g and 31P-hyperfine tensors agree with experiments for M = Mo, W. The anions adopt a slightly distorted pyramidal structure with PPh3 in basal position and the spin mostly delocalized in a metal-dz2 orbital and carbon-pz orbitals of carbonyls. The EPR tensors are slightly modified by annealing, they suggest that new constraints in the matrix distort the structure of [M(CO)4PPh3]•− (M = Cr, Mo, W).
